Electronics & Software
See the breakdown of the control system and interface of the project.
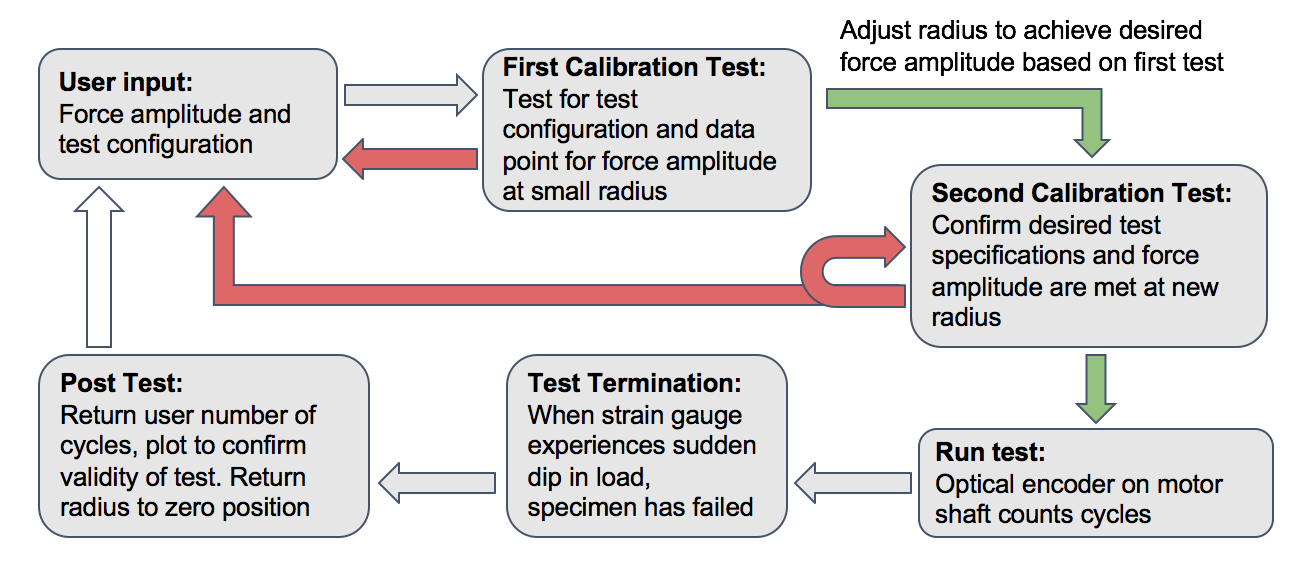
Control System:
The control system's purpose is to calibrate and move the adjustable radius to the proper location, record the data, and to turn off the motor upon completion of the test. This is done in a series of steps, explained by the flowchart below. The control system takes the desired force as an input, moves the radius accordingly, and outputs the load on the test specimen.
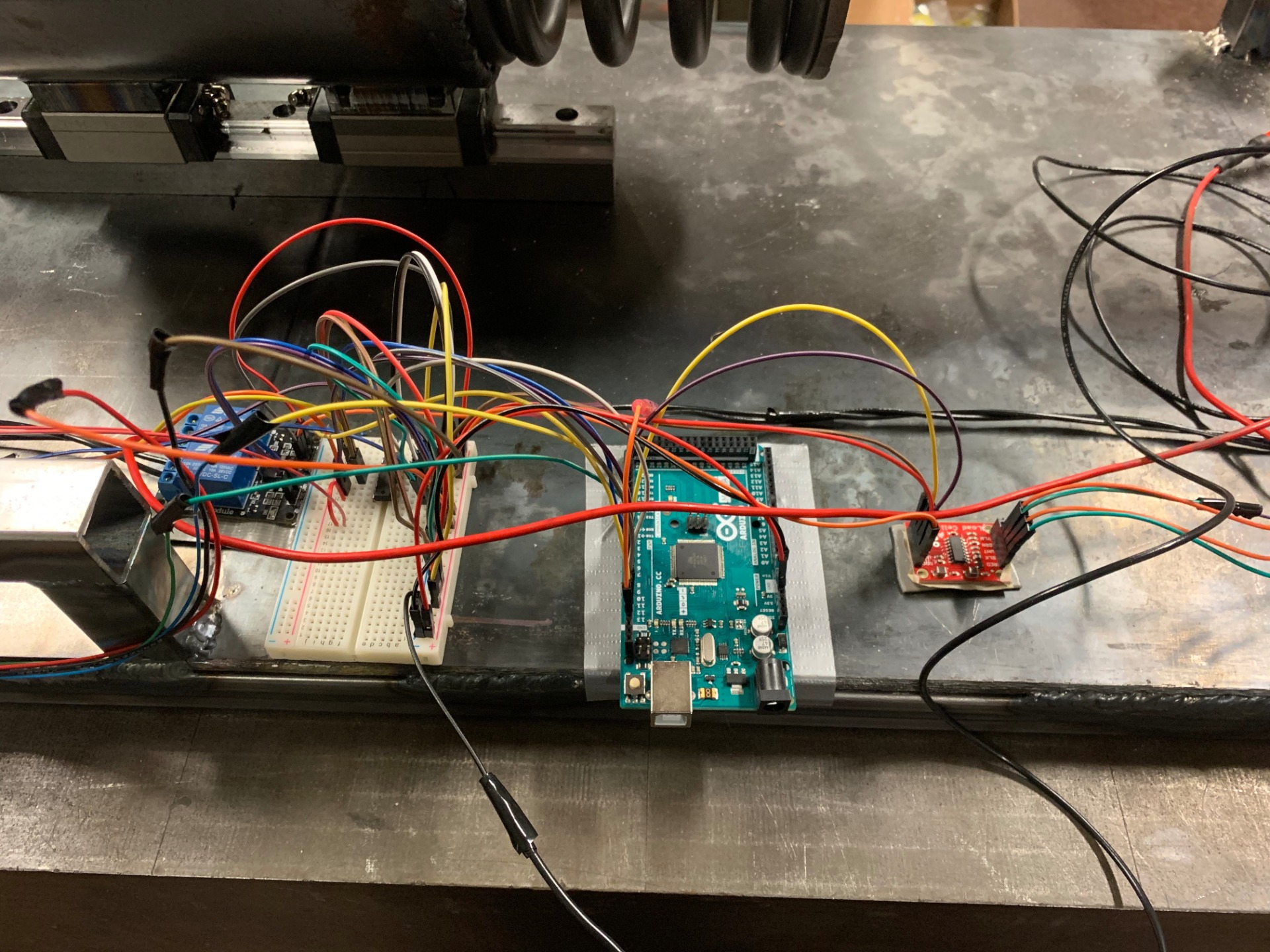
Schematic and Components:
The Arduino will be the center of the schematic, as it will be connected to the motor, stepper motor, and load cell. It will be connected to the motor by a relay, and will be taking the output from an optical encoder to count the cycles. It will connect to the stepper motor using an H-Bridge, which will serve as the controller for the stepper motor. The load cell will connect using a strain gauge amplifier, so the Arduino will know when to kill the motor. In total, we have the following components:
- Arduino Mega
- Strain Gauge
- Strain Gauge Amplifier
- Stepper Motor
- H-Bridge Stepper Motor Controller
- Optical Encoders
- Relay
- Slip Ring and wiring
Software and UI:
The software will be done in a combination of C and Matlab. The Arduino will require C code to control the stepper motor to move the radius. Arduino will also have code to switch the relay to turn off the motor. The Arduino will be plugged into a laptop, which will be running Matlab for the user interface and data processing after the test.